Medical Conditions
Hyperthyroidism
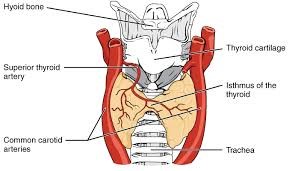
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland that is located in the lower front of the neck, just above the collarbone.
The role of the thyroid is to make thyroid hormones, which are released into the blood and then carried to every tissue in
the body. In children, thyroid hormone helps to ensure that growth and development occur normally, and that the body’s energy,
metabolism, heart, muscles, and other organs are working properly.
Hyperthyroidism refers to a disease in which there is
excessive amount of thyroid hormone in the blood. This is generally
caused by overproduction or release of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland.
Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Weight loss
- Excessive sweating and feeling too warm when others are comfortable
- Rapid heart rate and palpitations
- Poor school performance
- Mood swings, including irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Bulging or prominence of the eyes
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
Antithyroid Medications
The most common method of treatment of hyperthyroidism is administration of antithyroid medication, which stops the thyroid gland from making and releasing thyroid hormone. The drug of choice is methimazole.
Methimazole can be associated with side effects including an itchy skin rash (hives), and rarely joint and muscle pains and aches, jaundice (skin and eye yellowing from a liver problem), and a low white blood cell count, which might make it hard to fight infection. If one of these side effects occurs, another form of treatment must be used.
This medication may control the disease but will not cure it.
Radioactive Iodine
Radioactive iodine is safe to use as a treatment in young people.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the thyroid gland is also an effective way to treat hyperthyroidism. Risks include damage to the parathyroid glands, which are usually attached to the thyroid and control calcium in the blood, or damage to the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which is nearby and could lead to a hoarse voice.
Beta Blockers
In the early stage of treatment, beta blockers like propranolol or atenolol are used to increase the comfort level of the young person with hyperthyroidism. These drugs will not affect thyroid hormone levels but can help in general well-being by controlling symptoms like palpitations, tremors, and anxiety as well as rapid heart rate.
Hyperthyroidism Nutrition tips:
Foods to eat if you have hyperthyroidism:
Low-iodine foods
The mineral iodine plays a key role in making thyroid hormones. A low-iodine diet helps to reduce thyroid hormones. Add these foods to your daily diet:
- Non-iodized salt
- Weight loss
- Coffee or tea (without milk or dairy- or soy-based creamers)
- Egg whites
- Fresh or canned fruit
- Unsalted nuts and nut butters
- Homemade bread or breads made without salt, dairy, and eggs
- Popcorn with non-iodized salt
- Oats
- Potatoes
- Honey
- Maple syrup
- Cruciferous vegetables
Several nutrients are essential for thyroid health and to balance thyroid hormone production.
Iron
Iron is important for many vital bodily functions, including thyroid health. This mineral is needed for blood cells to carry oxygen to every cell in your body. Low levels of iron are linked to hyperthyroidism. Get plenty of iron in your diet with foods such as:
- Dried beans
- Green leafy vegetables
- Lentils
- Nuts
- Poultry, such as chicken and turkey
- Red meat
- Seeds
- Whole grain
Selenium
Selenium-rich foods may help to balance thyroid hormone levels and protect your thyroid from disease. Selenium helps to prevent cell damage and keep your thyroid and other tissues healthy. Good food sources of selenium include:
- Brazil nuts
- Tea
- Mushrooms
- Meat, such as beef and lamb
- Rice
- Oat bran
- Poultry, such as chicken and turkey
- Sunflower seeds
Zinc
Zinc helps you use food for energy. This mineral also keeps your immune system and thyroid healthy. Food sources of zinc include:
- Beef
- Chichpeas
- ocoa powder
- Cashews
- Mushrooms
- Pumpkin seeds
- Lamb
Calcium and vitamin D
Hyperthyroidism causes weak and brittle bones. Bone mass may be restored with treatment. Vitamin D and calcium are necessary for building healthy bones. Calcium-rich foods include:
- Spinach
- Collard greens
- White beans
- Kale
- Okra
- Calcium-fortified orange juice
- Almond milk
- Calcium-fortified cereals
Vitamin D is found in these low-iodine foods:
- Vitamin D-fortified orange juice
- Vitamin D-fortified cereals
- Beef liver
- Mushrooms
- Fatty fish
Healthy fats
Fats that are from whole foods and largely unprocessed may help reduce inflammation. This helps to protect thyroid health and balance thyroid hormones. Nondairy fats are important in a low-iodine diet. These include:
- Flaxseed oil
- Olive oil
- Avacado oil
- Coconut oil
- Sunflower oil
- Avacado
- Unsalted nuts and seeds
Spices
Some spices and herbs have anti-inflammatory properties to help protect and balance thyroid function. Add flavor and a dose of antioxidants to your daily meals with:
- Turmeric
- Green chilies
- Black pepper
Foods to avoid if you have hyperthyroidism
Excess iodine (Eating too many iodine-rich or iodine-fortified foods may lead to hyperthyroidism or worsen it in some cases.)
Seafood has the most iodine. Avoid the following commonly consumed seafood and seafood additives:
- Fish
- Seaweed
- Crabs
- Lobster
- Sushi
Caffeine
Foods and beverages that contain caffeine, such as coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate, can make the symptoms of hyperthyroidism worse and lead to increased anxiety, nervousness, irritability, and rapid heart rate.
If caffeine has this effect on you, then avoiding or limiting your intake may be a good option. Try replacing caffeinated beverages with natural herbal teas, flavored water, or hot apple cider.
© Copyright All Rights Reserved 2022